

This fair price will ensure that there will be no market inefficiencies in the long run.
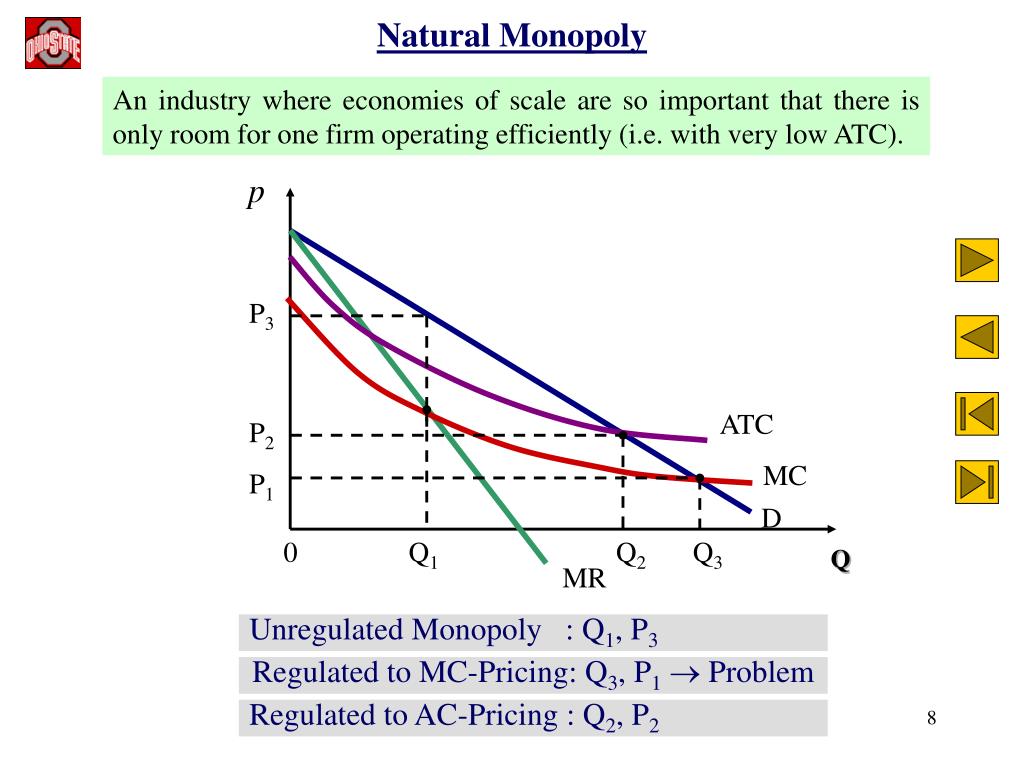
This means that the firm will make neither a profit nor a loss. With proper market assessment, the government will set the price at P G where the average total cost curve intersects the average revenue curve (which is also the demand curve). For instance, if the government sets the price ceiling at P C, it leaves the monopoly firm making a loss as this price is lower than the firm's average total costs, and the firm will not be able to sustain operations in the long run. It is challenging as the price shouldn't be set too low as doing will lead the firm to shut down. Now, the government needs to intervene to make sure the price is set at a fair level. The price is set very high and will lead to market inefficiencies if it is not regulated properly. In Figure 2, we can see that if a firm is not regulated, it produces the quantity of Q M and charges the price of P M. The barrier to entry in such a market can be due to government regulation, natural monopoly, or due to a single firm owning a rare resource that is not easily accessible to everyone. The monopoly has made it difficult for new firms to enter the market by exerting significant control over it. Sellers in a monopoly can affect the price of the product since they have no competitors and the products they sell cannot be easily substituted. Let's first review what a monopoly is and then go over the definition of a natural monopoly.Ī monopoly emerges when there is just one seller of a non-substitutable product in a market. Why do natural monopolies exist? Want to learn about natural monopoly and how the government should regulate it? Let's get straight into the article. Or would you? Don't start celebrating just yet because the government is likely to step in and control pricing. Due to your monopolistic status, you may be able to sell your products for a higher price even though you produce them at a cheaper cost. Price Determination in a Competitive MarketĬonsider that you are the only provider of public utilities with the capacity to provide the service at a very low cost in the overall industry.Market Equilibrium Consumer and Producer Surplus.Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand.Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Formula.Effects of Taxes and Subsidies on Market Structures.Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run.Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run.Behavioural Economics and Public Policy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
